The slide-line element may be used to impose kinematic constraints between nodes. Either perfect friction (i.e., "stick") or frictionless (i.e., "slip") conditions may be achieved.
A slide-line element is defined by three nodes and a spring constant or "penalty parameter," k. The connection from node A to node B defines the "slide-line" direction, and node C is the contact node (see Fig. 9.6.1).

Figure 9.6.1 Slide Line
The projected distance of node C to node A onto the slide-line direction is denoted by a, and is given by
a
= AB . AC / (AB . AB) 0 ![]() a
a ![]() 1
1
where "." denotes the dot product of two vectors. The direction of the unit vector n normal to the slide-line direction is given by:
n = (AB x AC) x AB / |(AB x AC) x AB|
where "x" denotes the cross product of two vectors. The local contact stiffness matrix K is given by

where the rows and columns are arranged such that the first, second and third rows (columns) correspond to nodes A, B and C, respectively. If k > 0 is sufficiently large, the point C will be forced to lie (approximately) on the slide-line AB. The contact/release condition is defined as follows:
0 ![]() a
a ![]() 1 contact
1 contact
otherwise, release.
When contact is noted, a contact element stiffness and out-of-balance force are added to the global equations. These arrays are defined as follows:
Stiffness Matrix: (three-dimensional case)

K(slip) = RTKR
where
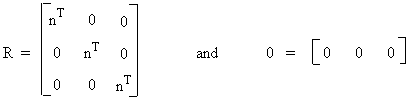
Out-of-Balance
Force

SLIDE_LINE
Element_name = SLIDE_LINE stick = on, etc...
m, stiff( m) < m = 1, numat >
< connectivity data >
< terminate with a blank record >
9.6.1 Element Group Control
Information
Must follow the element name (same
data record), and define the control parameters as follows:
Note Variable Name Type Default Description
(1) stick list [on] Contact condition
on / off
formulation list [penalty] Formulation
penalty
augmented_lagrangian
Notes/
(1) The contact condition may be either perfect friction (i.e. "stick") or frictionless (i.e. "slip"). In the stick case, no relative motion is allowed between nodes when in contact. In the slip case, frictionless sliding is allowed on the slide-line.
9.6.2 Geometric
/ Material Properties Data (Numat sets)
Note Variable Default Description
M [0] Geometric/material set number
STIFF(M) [0.0] Spring constant k (i.e. "penalty parameter")
9.6.3 Element Nodal Connectivity Data
Consult Chapter 11 for details; for this element NEN = 3, and the nodes are entered in the following order; nodeA, nodeB, nodeC (see Figure 9.6.1).
Notes . .