9.11††††††† Multi_Point_Constraints
9.11.1†††† Multi_Point_Constraint
†††††††††††††† The element is used to impose linear multi nodal point
constraint conditions.† A typical
constraint equation is written as:


Where the 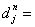 †are the selected nodal
point degrees of freedom j at node n.†
Constraints may originate from several kinds of physical specifications,
such as skewed nodal displacement boundary conditions, interface conditions
between regions (solid-solid contact, fluid-solid interactions), etc.† An augmented lagrangian formulation with
penalty regularization is used to satisfy the constraints.† Uzawa's algorithm is used to update the
lagrange multipliers. A load time function (ltime) can be used to vary
†are the selected nodal
point degrees of freedom j at node n.†
Constraints may originate from several kinds of physical specifications,
such as skewed nodal displacement boundary conditions, interface conditions
between regions (solid-solid contact, fluid-solid interactions), etc.† An augmented lagrangian formulation with
penalty regularization is used to satisfy the constraints.† Uzawa's algorithm is used to update the
lagrange multipliers. A load time function (ltime) can be used to vary with time.
with time.
MULTI_POINT_CONSTRAINT
††††††††††† Element_name =
MULTI_POINT_CONSTRAINT
††††††††††† m,††
ltime(m), penalty(m),††
c0(m),†† ( idof(i,m), c(i,m), i=1,ndof
)
††††††††††††††††† < connectivity data >
††††††††††††††††† < terminate with a blank
record >.
EXAMPLE
††††††††††† Define_element_group†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† name
= "mpc"†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† element_name
= multi_point_constraint†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† element_type
= interface†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† number_of_coeff_1
=† 3 ††/
††††††††††††††††††††††† number_of_material_sets
= 1
††††††††††† c††††††††† m†††††††† ltime††††††††††††††† penalty†† c0††††††††††††††† (idof, c1)††††† (idof, c2)††††††† (idof,
c3)
††††††††††††††††††††††† 1††††††††† 2†††††††††††††††††††††
1 e+3†††† 1.0††††††††††††††† † 1, 1.0††††††††† †
1, -1.0 † †††††††††††2, -1.0
††††††††††† Nodal_connectivity†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† input_format
= list
††††††††††††††††††††††† 1††††††††† 1††††††††† 1††††††††† †
5††††††† 0
††††††††††††††††††††††† 2††††††††† 1††††††††† 6††††††††† 10††††††† 9
In this case the element is used to impose the following
constraints:
††††††††††† at nodes 1
and 5:†††††††† 
††††††††††† at nodes 6,
9 and 10:†† 
References /
Bibliography
1.†††† Arrow, K.J.,
Hurwicz, L. and Uzawa, H., Studies in
Nonlinear Programming, Stanford
University Press,
Stanford, 1958.
9.11.1.1† Element
Control Information
Note††††††††† Variable
†††† †††††††††††††Type††††††††††††† †† †††Default††††† ††††††††††† Description
††††††††††† Element_name†††† †††††††
††list†††††††††††††††† ††† †††††††[*]†††††††† ††††††††††† Multi_point_constraint
††††††††††† Element_type†††††† †††††††
††list†††††††††††††††† ††††† [interface]† ††††††††††† Element_type
††††††††††† Element_shape†††† ††††††
†††list†††††††††††††††† † ††††††[none]††††† ††††††††††† Element_shape
'
††††††††††† Number_of_coeff_1 ††† †integer†††††††††† [max
[3, 1 + ndof]]†††† Number of coefficients
ciís
††† Number_of_material_sets ††† integer††††††††††† †††††††† [0.0]††††††† ††††††††††† Number_of_material_sets
9.11.1.2† Material
Properties (Numat sets)
Note††††††††† Variable†††††††††† Default††††††††††††††††† Description
††††††††††††††††††††† M††††††††††††††††††† [0]††††††††††††††††††††† Geometric/material set number
††††††††††† † LTIME(M)††††††††††††† [0]††††††††††††††††††††† Load-time function number
††††††††††† PENALTY(M)††††††† [0.0]††††††††††††††††††† Penalty
coefficient
†††††††††††††††††† C0(M)†††††††††††††† [0.0]††††††††††††††††††† Coefficient 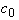
†††††††††††††† IDOF(i,M)†††††††††††† [0]††††††††††††††††††††† Degree
of freedom number j
†††††††††††††††††† C(i,M)†††††††††††††† [0.0]††††††††††††††††††† Coefficient 
9.11.1.3† Nodal
Connectivity Data
††††††††††† Consult
Chapter 11 for details; for this element NEN = †number_of_coeff_1
9.11.2†††† Multi_Point_BC
†††††††††††††† The element is used to impose linear multi nodal point
constraint conditions.† A typical
constraint equation is written as:
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††††††††††††††††††††† 

Where the 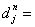 †are the selected nodal
point degrees of freedom j at node n.†
Constraints may originate from several kinds of physical specifications,
such as skewed nodal displacement boundary conditions, interface conditions
between regions (solid-solid contact, fluid-solid interactions), etc.† An augmented lagrangian formulation with
penalty regularization is used to satisfy the constraints.† Uzawa's algorithm is used to update the
lagrange multipliers. A load time function (ltime) is used to apply the
constraint as a function of time.
†are the selected nodal
point degrees of freedom j at node n.†
Constraints may originate from several kinds of physical specifications,
such as skewed nodal displacement boundary conditions, interface conditions
between regions (solid-solid contact, fluid-solid interactions), etc.† An augmented lagrangian formulation with
penalty regularization is used to satisfy the constraints.† Uzawa's algorithm is used to update the
lagrange multipliers. A load time function (ltime) is used to apply the
constraint as a function of time.
MULTI_POINT_BC
††††††††††† Element_name = MULTI_POINT_BC
††††††††††† m,††
ltime(m), penalty(m),††
c0(m),†† ( idof(i,m), c(i,m), i=1,ndof
)
††††††††††††††††† < connectivity data >
††††††††††††††††† < terminate with a blank
record >.
EXAMPLE
††††††††††† Define_element_group†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† name
= "mpc"†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† element_name
= multi_point_BC†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† element_type
= interface†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† number_of_coeff_1
= 3† †/
††††††††††††††††††††††† number_of_material_sets
= 1
††††††††††† c††††††††† m†††††††† ltime††††††††††††††† penalty†† c0††††††††††††††† (idof, c1)††††† (idof, c2)††††††† (idof,
c3)
††††††††††††††††††††††† 1††††††††† 2†††††††††††††††††††††
1 e+3†††† 1.0††††††††††††††† † 1, 1.0††††††††† †
1, -1.0 † †††††††††††2, -1.0
††††††††††† Nodal_connectivity†† /
††††††††††††††††††††††† input_format
= list
††††††††††††††††††††††† 1††††††††† 1††††††††† 1††††††††† †
5††††††† 0
††††††††††††††††††††††† 2††††††††† 1††††††††† 6††††††††† 10††††††† 9
In this case the element is used to impose the following
constraints:
††††††††††† at nodes 1
and 5:†††††††† 


††††††††††† at nodes 6,
9 and 10:†† 

References /
Bibliography
1.†††† Arrow, K.J.,
Hurwicz, L. and Uzawa, H., Studies in
Nonlinear Programming, Stanford
University Press,
Stanford, 1958.
9.11.2.1† Element
Control Information
Note††††††††† Variable
†††† †††††††††††††Type††††††††††††† ††††† Default††††† ††††††††††† Description
††††††††††† Element_name†††† †††††††††
list†††††††††††††††† †††† ††††††[*]†††††††† ††††††††††† Multi_point_BC
††††††††††† Element_type†††††† †††††††††
list†††††††††††††††† ††††† [interface]† ††††††††††† Element_type
††††††††††† Element_shape†††† †††††††††
list†††††††††††††††† ††††††† [none]††††† ††††††††††† Element_shape
††††††††††† Number_of_coeff_1 †††† integer†††††††††† [max [3, 1 + ndof]]†††† Number of coefficients ciís
†††
Number_of_material_sets ††† integer††††††††††† †††††††† [0.0]††††††††††††††††††† Number_of_material_sets
9.11.2.2† Material
Properties (Numat sets)
Note††††††††† Variable†††††††††† Default††††††††††††††††† Description
††††††††††††††††††††† M††††††††††††††††††† [0]††††††††††††††††††††† Geometric/material set number
††††††††††† LTIME(M)††††††††††††††† [0]††††††††††††††††††††† Load-time function number
††††††††††† PENALTY(M)††††††† [0.0]††††††††††††††††††† Penalty
coefficient
†††††††††††††††††† C0(M)†††††††††††††† [0.0]††††††††††††††††††† Coefficient 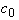
†††††††††††††† IDOF(i,M)†††††††††††† [0]††††††††††††††††††††† Degree
of freedom number j
†††††††††††††††††† C(i,M)†††††††††††††† [0.0]††††††††††††††††††† Coefficient 
9.11.2.3† Nodal
Connectivity Data
††††††††††† Consult
Chapter 11 for details; for this element NEN = number_of_coeff_1
![]()
![]()
![]() †are the selected nodal
point degrees of freedom j at node n.†
Constraints may originate from several kinds of physical specifications,
such as skewed nodal displacement boundary conditions, interface conditions
between regions (solid-solid contact, fluid-solid interactions), etc.† An augmented lagrangian formulation with
penalty regularization is used to satisfy the constraints.† Uzawa's algorithm is used to update the
lagrange multipliers. A load time function (ltime) can be used to vary
†are the selected nodal
point degrees of freedom j at node n.†
Constraints may originate from several kinds of physical specifications,
such as skewed nodal displacement boundary conditions, interface conditions
between regions (solid-solid contact, fluid-solid interactions), etc.† An augmented lagrangian formulation with
penalty regularization is used to satisfy the constraints.† Uzawa's algorithm is used to update the
lagrange multipliers. A load time function (ltime) can be used to vary![]() with time.
with time.![]()
![]()
