10.17 Scalar_Diffusion_Model: Generalized Scalar Diffusion Model
SCALAR_DIFFUSION
Material_name = SCALAR_DIFFUSION
Material_set_number = mset , etc...
The generalized scalar diffusion model is defined as follows.
Note Variable Name Type Default Description
Material_set_number integer [1] Material set number ![]() Numat
Numat
Matrix_mass_density real [0.0] Matrix mass density ![]()
Matrix_compressibility real [0.0] Matrix compressibility ![]()
Grains_compressibility real [0.0] Grains compressibility ![]()
Fluid_mass_density real [0.0] Mass density ![]() (fluid phase)
(fluid phase)
Fluid_compressibility real [0.0] Compressibility![]() [LT2 / M]
[LT2 / M]
Fluid_viscosity real [0.0] Viscosity ![]() [M / L T]
[M / L T]
(1) Ideal_fluid list [off] Ideal fluid/gas option
on / off
Reference_pressure real [0.0] Reference pressure
Reference_temperature real [0.0] Reference temperature
Molecular_mass real [0.0] Molecular mass of fluid/gas
Porosity real [0.0] Porosity
Material_type list [linear] Material type
linear / nonlinear
Number_of_phases integer [1] Number of phases; Nphase
Max_number_of_data_points integer [0] Maximum number of data points used to
define relative permeability/capillary
pressure
(cont’d)
Note Variable Name Type Default Description
•
Permeability
Permeability list [none] Permeability
Type list [*] Form of permeability matrix:
isotropic / anisotropic if isotropic only k11 need be specified.
(2) Name list [*] Name of permeability:
conductivity hydraulic conductivity [L / T]
mobility mobility [L3 T / M]
intrinsic intrinsic permeability [L2]
k_11 real [0.0] Permeability k11
k_22 real [0.0] Permeability k22
k_33 real [0.0] Permeability k33
k_12 real [0.0] Permeability k12
k_23 real [0.0] Permeability k23
k_13 real [0.0] Permeability
k13
(3) Exponent_porosity real [0.0] Porosity exponent
•
Diffusivity / Dispersivity
Diffusivity list [none] Diffusivity
Type list [*] Form of diffusivity matrix:
isotropic / anisotropic if isotropic only k11 need be specified.
k_11 real [0.0] Diffusivity k11
k_22 real [0.0] Diffusivity k22
k_33 real [0.0] Diffusivity k33
k_12 real [0.0] Diffusivity k12
k_23 real [0.0] Diffusivity k23
k_13 real [0.0] Diffusivity
k13
EXAMPLE
Scalar_Diffusion_Model /
material_type = linear /
material_name = scalar_diffusion
material_set_number = 1 /
mass_density = 1.e3 /
porosity = 0.30 /
compressibility = 1.e3-6 /
permeability /
type = isotropic /
name = conductivity /
k_11 = 1.60e-3
Notes /
(1) The equation of state is then of the form:
p
= ![]()
where p = pressure; ![]() = mass density; R = fluid/gas constant (=8314
J/(kmol°K)); w = molecular mass; and T = temperature [°K]. Then, for instance for air:
= mass density; R = fluid/gas constant (=8314
J/(kmol°K)); w = molecular mass; and T = temperature [°K]. Then, for instance for air:
w = 28.97 kg/kmol, and:
![]()
(2) Let k denote the intrinsic permeability (units: [L2]). Then
![]() = hydraulic conductivity [L / T]
= hydraulic conductivity [L / T]
![]() = mobility [L3
T / M]
= mobility [L3
T / M]
where ![]() = viscosity [M /
L T],
= viscosity [M /
L T], ![]() = fluid mass density
[M / L3]; and g =
acceleration of gravity [L / T2].
= fluid mass density
[M / L3]; and g =
acceleration of gravity [L / T2].
(3) The permeability is function of porosity as:
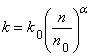
where ![]() initial porosity, and
initial porosity, and ![]() porosity exponent.
porosity exponent.
10.17.1 Multi-Phase Fluid Flow
For multi-phase fluid flow problems
the following material data must also be provided.
Note Variable Name Type Default Description
eos_options list [none] Equation of state options
PU_cmi
tough2
Peng_Robinson
dry_gas
reference_pressure real [0.0] reference pressure
reference_temperature real [0.0] reference temperature
matrix_mass_density real [0.0] Matrix mass density ![]()
matrix_compressibility real [0.0] Matrix compressibility ![]()
grains_compressibility real [0.0] Grains compressibility ![]()
(1) Relative_permeability list [*] Relative permeability formula ![]()
Touma_Vauclin
Linear
Power
Corey
Grant
perfect_mobility
Fatt_Klikoff
vanGenuchten_Mualem
Verma
Modified_Corey
Stone_3_phase
(1) rp_i real [0.0] Coefficient RP(i)
(cont’d)
Note Variable Name Type Default Description
(2) Capillary_pressure list [none] Capillary pressure formula
Touma_Vauclin
Linear
Pickens
Trust
Milly
Leverett
vanGenuchten
none
(2) cp_i real [0.0] Coefficient CP(i)
Notes /
(1) Relative Permeability Functions
IRP = 0 Touma_Vauclin function
The relative permeability is assumed in this case to be given by a curve fit to the experimental data as:
formula_type = 1 ![]()
formula_type = 2 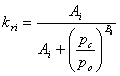
where pc = p2 –p1 = capillary pressure; p0 = normalizing pressure;
and Si = degree of saturation.
IRP = 1 linear function
krl increases linearly from 0 to 1 in the range RP(1) ≤ Sl ≤ RP(3);
krg increases linearly from 0 to 1 in the range RP(2) ≤ Sg ≤ RP(4).
Restrictions: RP(3) > RP(1); RP(4) > RP(2).
IRP = 2 Power function
krl = Sl**RP(1)
krg = 1.
IRP = 3 Corey’s curves (1954)
krl = Ŝ4
krg = (1 – Ŝ)2 (1 – Ŝ2)
where Ŝ =
(Sl – Slr) / (1 – Slr – Sgr)
with Slr = RP(1); Sgr = RP(2)
Restrictions: RP(1) + RP(2) < 1.
IRP = 4 Grant’s curves (Grant, 1977)
krl = Ŝ4
krg = 1 - krl
where Ŝ =
(Sl – Slr) / (1 – Slr – Sgr)
with Slr = RP(1); Sgr = RP(2)
Restrictions: RP(1) + RP(2) < 1.
IRP = 5 all phases perfectly mobile
krg = krl = 1 for all saturations; no parameters
IRP = 6 functions of Fatt and Klikoff (1959)
krl = (S*)3
krg = (1 – S*)3
where S* =
(Sl – Slr) / (1 – Slr)
with Slr = RP(1).
Restriction: RP(1) < 1.
IRP = 7 van Genuchten-Mualem model (Mualem, 1976; van Genuchten, 1980)

Gas relative permeability can be chosen as one of the following two forms, the
second of which is due to Corey (1954)
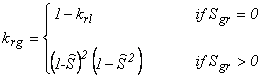
subject to the restriction 0 ≤ krl, krg ≤ 1
Here,
S* = (Sl – Slr) / (Sls – Slr), Ŝ = (Sl
– Slr) / (1 – Slr – Sgr)
Parameters: RP(1) = ![]()
RP(2) = Slr
RP(3) = Sls
RP(4)
= Sgr
Notation: Parameter ![]() is m in van Genuchten’s
notation, with m = 1 – 1/n;
is m in van Genuchten’s
notation, with m = 1 – 1/n;
parameter n is
often written as ![]() .
.
IRP = 8 function of Verma et al. (1985)
krl = Ŝ3
krg = A + B Ŝ + C Ŝ2
where Ŝ =
(Sl – Slr) / (Sls – Slr),
Parameters as measured by Verma et al. (1985) for steam-water flow in an
unconsolidated sand:
|
Slr = RP(1) = 0.2 |
B = RP(4) = -1.7615 |
|
Sls = RP(2) = 0.895 |
C = RP(5) = 0.5089 |
|
A = RP(3) = 1.259 |
|
IRP = 12 modified Corey function
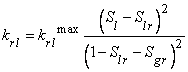
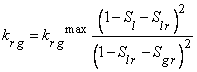
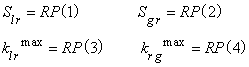
IRP = 14 Stone 3-phase model
a. Aqueous phase:
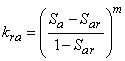
with ![]() irreducible aqueous phase saturation (typically
irreducible aqueous phase saturation (typically ![]() )
)
m = exponent (typically m=3).
b. Liquid phase:
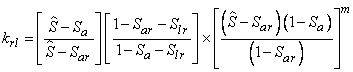
![]()
![]() irreducible liquid phase saturation (typically
irreducible liquid phase saturation (typically ![]() .
.
c. Gas phase:
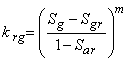
![]() irreducible gas phase saturation (typically
irreducible gas phase saturation (typically ![]() 0.01).
0.01).
Parameters: RP(1) = m
RP(2)
= ![]()
RP(3)
= ![]()
RP(4)
= ![]()
(2) Capillary Pressure Functions
ICP = 0 Touma_Vauclin function
The capillary pressure vs saturation is assumed in this case to be given by a van Genuchten-type curve fit to the experimental data as:
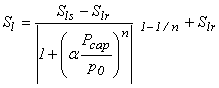
where Pcap = p2 - p1 = capillary pressure; p0 = normalizing pressure;
and Sl = degree of saturation.
Parameters: Slr = CP(1) Sls = CP(2) n = CP(3) α = CP(4) p0 = CP(5)
ICP = 1 linear function
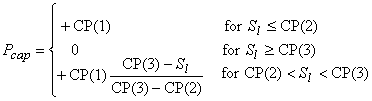
Restriction: CP(3) > CP(2).
ICP = 2 function of Pickens et al. (1979)
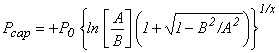
with
A = (1 +
Sl/Sl0) (Sl0 - Slr)
/ (Sl0 + Slr)
B = 1 – Sl/Sl0
where
P0 = CP(1) Slr = CP(2) Sl0 = CP(3) x = CP(4)
Restrictions: 0 < CP(2) < 1 ≤ CP(3); CP(4) ≠ 0
ICP = 3 TRUST capillary pressure (Narasimhan et al., 1978)
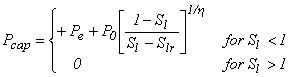
where
P0 = CP(1) Slr = CP(2)
![]() = CP(3) Pe = CP(4)
= CP(3) Pe = CP(4)
Restrictions: CP(2) ≥ 0; CP(3) ≠ 0
ICP = 4 Milly’s function (Milly, 1982)
Pcap = +97.783 x 10A
with
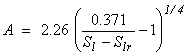
where Slr = CP(1)
Restriction: CP(1) ≥ 0.
ICP = 6 Leverett’s function (Leverett, 1941; Udell and Fitch, 1985)
![]()
with
![]() (T) = surface tension of water (supplied internally)
(T) = surface tension of water (supplied internally)
f(Sl) = 1.417 (1 – S*) – 2.120
(1 – S*)2 + 1.263
(1 – S*)3
where
S* = (Sl - Slr) / (1 – Slr)
Parameters: P0 = CP(1) Slr = CP(2)
Restriction: 0 ≤ CP(2) < 1
ICP = 7 van Genuchten function (van Genuchten, 1980)
![]()
subject to the restriction
0 ≤
Pcap ≤ Pmax
Here,
S* = (Sl - Slr) / (Sls
– Slr)
Parameters: CP(1) = ![]() = l – l/n
= l – l/n
CP(2) = Slr (should be chosen smaller than the corresponding
parameter in the relative permeability function; see
note below.)
CP(3)
= P0
CP(4)
= Pmax
CP(5)
= Sls
Notation: Parameter ![]() is m in van Genuchten’s
notation, with m = l – l/n;
is m in van Genuchten’s
notation, with m = l – l/n;
parameter n is
often written as![]() .
.
Note
on parameter choices: In van Genuchten’s derivation (1980), the parameter Slr for irreducible water saturation
is the same in the relative permeability and capillary pressure functions. As a consequence, for Sl → Slr we have krl → 0 and Pcap → ![]() , which is unphysical because it implies that the radii of
capillary menisci go to zero as liquid phase is becoming immobile
(discontinuous). Accordingly, we
recommend to always choose a smaller Slr for the capillary pressure as compared to the
relative permeability function.
, which is unphysical because it implies that the radii of
capillary menisci go to zero as liquid phase is becoming immobile
(discontinuous). Accordingly, we
recommend to always choose a smaller Slr for the capillary pressure as compared to the
relative permeability function.
ICP = 8 no capillary pressure
Pcap = 0 for all saturations; no parameters
Note Variable Name Type Default Description
(1) Phase_number integer [1] Phase number; i ≤ Nphase
Phase_type list [liquid] Phase type
liquid
gas
Phase_name string [none] Phase name; name(s) must be enclosed
in quotation marks.
Mass_density real [0.0] Mass density ![]()
Compressibility real [0.0] Compressibility![]() [LT2 / M]
[LT2 / M]
Viscosity real [0.0] Viscosity ![]() M / L T
M / L T
Saturation real [0.0] Saturation Si
Minimum_saturation real [0.0] Minimum saturation Sir
Maximum_saturation real [0.0] Maximum saturation Sis
(2) formula_type integer [iphase] Relative permeability formula type
(Touma_Vauclin option)
(2) a_coefficient real [0.0] Coefficient Ai in curve fit formula
(2) b_coefficient real [0.0] Coefficient Bi in curve fit formula
(2) Normalizing_pressure real [0.0] Normalizing pressure po in curve fit
formula
•
Diffusivity / Dispersivity
Diffusivity list [none] Diffusivity
Type list [*] Form of diffusivity matrix:
isotropic / anisotropic if isotropic only k11 need be specified.
k_11 real [0.0] Diffusivity k11
k_22 real [0.0] Diffusivity k22
k_33 real [0.0] Diffusivity k33
k_12 real [0.0] Diffusivity k12
k_23 real [0.0] Diffusivity k23
k_13 real [0.0] Diffusivity
k13
Notes/
(1) The wetting phase must be defined as phase_number = 1.
(2) The relative permeability is assumed in this case to be given by a curve fit to the experimental data as:
formula_type = 1 ![]()
formula_type = 2 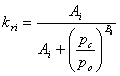
where pc = p2 –p1 = capillary pressure; p0 = normalizing pressure; and Si = degree of saturation.
References / Bibliography
1. Touma, J. and M. Vauclin, “Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Two-Phase Infiltration in a Partially Saturated Soil,” Transport in Porous Media, Vol. 1, 1986, pp. 27-55.
10.17.1.2 Relative Permeability and Capillary Pressure
Data
Note Variable Name Type Default Description
Material_set_number integer [1] Material set number ![]() Numat
Numat
Data_type list [none] Data type:
Relative_permeability Relative permeability
Capillary_pressure Capillary pressure
•
Relative Permeability Case
Data must follow in the form:
(1) < S1, kr1(S1) , kr2 (S1) >
< etc..., terminate with a blank record >
• Capillary Pressure Case
Data must follow in the form:
(2) < S1, pc1(S1), pc2(S1) >
< etc..., terminate with a blank record >
Notes /
(1) S1 = degree of saturation for phase 1; S2 = 1 - S1
kr1 (S1) = relative permeability for phase 1
kr2 (S1) = relative permeability for phase 2
(2) pc1 (S1) = capillary pressure for phase 1 invasion
pc2 (S1) = capillary pressure for phase 1 drainage
EXAMPLE
Scalar_diffusion_model /
material_type = linear /
material_name = scalar_diffusion /
number_of_phases = 2 /
max_number_of_data_points = 11
material_set_number = 1 /
porosity = 0.30 /
permeability /
type = isotropic /
name = intrinsic /
k_11 = 2.1248e-11
phase_number = 1 /
mass_density = 62.4 /
compressibility = 1.0e-6 /
viscosity = 2.088543e-5
phase_number = 2 /
mass_density = 49.92 /
compressibility = 1.0e-6 /
viscosity = 8.3541723e-5
material_set_number = 1 /
data_type = Relative_permeability
0.20 0.00 0.60
0.25 0.02 0.47
0.30 0.04 0.38
0.35 0.07 0.31
0.40 0.09 0.25
0.45 0.13 0.18
0.50 0.17 0.13
0.55 0.22 0.09
0.60 0.28 0.05
0.65 0.35 0.02
0.70 0.45 0.00
material_set_number = 1 /
data_type = Capillary_pressure
0.200 208.854 208.854
0.225 173.349 173.349
0.250 148.287 148.287
0.300 121.136 121.136
0.350 102.339 102.339
0.400 87.719 87.719
0.500 68.922 68.922
0.650 52.213 52.213
0.700 48.663 48.663
Notes . .