12.1 Define Solution Staggers
(Optional)
The procedure allows the use of a multistagger solution
strategy in which the full system of coupled equations defined in the problem
domain is partitioned into smaller subsystems of equations. Each subsystem is then solved separately
assuming that the unknown variables of the other subsystems are temporarily
frozen. The equation subsystems are
referred to as "staggers," and the approach amounts to a partial
decoupling of the full system of coupled equations. Each stagger is assigned its own
time-stepping parameters, nonlinear iteration procedure, linear equation solver
and/or eigen solver. In each stagger,
the active variables are solved while all the other variables belonging to the
other staggers are held fixed. In turn,
after update of the solution variables of the current stagger, they are held
fixed when solving for the variables of the subsequent staggers. The staggers are solved sequentially and repeatedly
in a predetermined sequence until they all have converged to a self consistent
set of solution variables. The iterative
procedure is handled by the Stagger_control command. The procedure is equivalent to solving the
coupled system (see e.g. [1-5]).
Solution staggers may also be used to selectively solve for the
equations defined in various parts of the mesh. Element groups belonging to the
same region cannot be assigned to the same solution stagger.
12.1.1 Define Staggers
DEFINE_STAGGER
DEFINE_STAGGER name =
"<string>", etc...
Set up solution staggers to
use for solving the equations defined in the problem.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name
|
string
|
[none]
|
Stagger name
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name must be enclosed in quotation marks.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
Element_group(s)
|
string
|
[none]
|
Element groups belonging to the stagger.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name(s) must be enclosed in
quotation marks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable
|
list
|
[all]
|
Active variable selection for the stagger:
|
|
|
all
|
|
|
All degrees of freedom
Solid
displacement
Solid
displacement and rotation
Fluid velocity
Fluid velocity
and pressure
Temperature
Potential
Electric
potential
Pressure
Scalar transport
Level set
Stream function
Coupled porous
continuum (hyperbolic)
Coupled continuum
(parabolic)
Coupled
thermo-solid continuum
ALE mesh motion
|
|
|
solid_displacement
solid_displacement_and_rotation
fluid_velocity
fluid_velocity_and_pressure
temperature
potential
electric_potential
pressure
scalar_transport
level_set
stream_fct
solid_displacement_and_fluid_velocity
solid_displacement_and_fluid_pressure
solid_displacement_and_temperature
mesh_motion
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(cont’d)
(cont’d)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Activation_time
|
real
|
[0.0]
|
Time at which stagger becomes active
|
|
|
Deactivation_time
|
real
|
[0.0]
|
Time at which stagger becomes inactive
(only active if
deactivation_time >
activation_time)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
External_loads
|
string
|
[on]
|
External loads option
|
|
|
on / off
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nodal_loads
|
string
|
[on]
|
Nodal loads option
|
|
|
on / off
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Surface_loads
|
string
|
[on]
|
Surface loads option
|
|
|
on /
off
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heat_loads
|
string
|
[on]
|
Heat loads option
|
|
|
on / off
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
string
|
[off]
|
Multi-flow initialization (viz., p2 = p1)
|
|
|
on / off
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2)
|
Time_integration
|
command
|
[none]
|
Time integration parameters
used in the stagger
|
|
|
Nonlinear_iterations
|
command
|
[none]
|
Nonlinear iterations used in
the stagger
|
|
|
Linear_solver
|
command
|
[none]
|
Linear solver used in the stagger
|
|
|
Eigen_solver
|
command
|
[none]
|
Eigen solver used in the stagger
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXAMPLE
Define_stagger / #
define a solution stagger
name =
"stagger1" / # set
name
element_group(s) = / #
include element groups 1 and 2
"Group1"
, "Group2" /
time_integration / #
time integration parameters,
etc...
equation_type = ... ,
etc...
Notes/
(1) List all element group names or numbers
belonging to the solution stagger.
Element groups belonging to the same region cannot be assigned to the
same solution stagger.
(2) The requested analysis parameters may be
entered directly without use of the main commands keywords.
12.1.2 Staggers Control
STAGGER_CONTROL
STAGGER_CONTROL name = "<string>", etc...
The staggers are solved
sequentially and repeatedly in a predetermined sequence until they all have
converged to a self consistent set of solution variables. The iterative procedure is handled by the
stagger_control command. When solution
staggers are used to selectively solve for the equations defined in various
parts of the mesh, then an interface between the various physical solution
domains will be defined.
Name string [none] Stagger name
Name
must be enclosed in quotation
marks
Balance_of_mass string [off] Balance of mass option
on / off
Coupling string [on] Coupling
option
on / off
Interface string [on] Interface
option
on / off
Max_number_of_iterations integer [0] Maximum number of iterations
Min_number_of_iterations integer [0] Minimum number of iterations
Convergence_check list [on] Convergence check
on / off
Convergence_tol_sol real [1.E-3] Convergence tolerance for solution
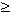 0.0
0.0
Convergence_tol_mass real [0.0] Convergence tolerance for mass (in %)
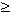 0.0
0.0
EXAMPLE
Stagger_control /
max_number_of_iterations
= 5 /
convergence_check
= on
References / Bibliography
1. Farhat, Charbal, K.C. Park
and Yves DuBois-Pelerin, "An Unconditionally Stable Staggered Algorithm
for Transient Finite Element Analysis of Coupled Thermoelastic Problems," Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 85, (1991), 349-365.
2. Felippa,
C.A. and K.C. Park,
"Staggered transient analysis procedures for coupled mechanics problems:
formulation," Comp. Meth. Appl.
Mech. Eng., 24, (1980), 61-111.
3. Park,
K.C.,"Partitioned transient analysis procedures for coupled field
problems: stability analysis", J.Appl.
Mech., 47, (1980), 370-376.
4. Park, K.C. and C.A.
Felippa,"Partitioned transient analysis procedures for coupled field
problems: accuracy analysis", J.
Appl. Mech., 47, (1980),
919-926.
5. Prevost, J. H.,
"Partitioned Solution Procedure for Simultaneous Integration of
Coupled-Field Problems," Comm. Num.
Meth. Eng., 13, No.
4, (1997), pp. 239-247.
Notes . .
![]() 0.0
0.0![]() 0.0
0.0