Fuel Cell Electrode
Diagram
This
picture contains active zones.
Click and explore!
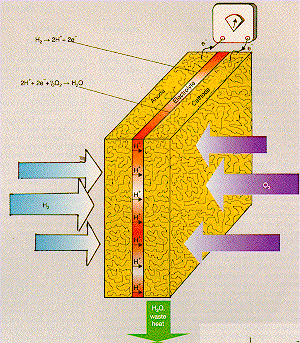
A diagram of one electrode
pair is shown
opposite. Hydrogen and oxygen are supplied
to the
cell as molecular gases which are
dissociated by catalyst material on the
electrodes.
At the Anode (negative electrode) hydrogen gas
is
dissociated into two protons (H+) and two
electrons (e_).
The protons can travel through
the polymeric proton exchange membrane:
PEM
(a solid electrolyte) and combine with
oxygen ions generated at
the Cathode
(positive electrode) to form water.
| Menu |
| Prev |
| Next |