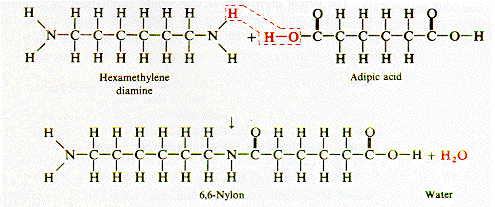
Macromolecules may also be formed in a 'condensation polymerization' reaction in which more than one monomer type takes part in the sequential polymerization reaction and a product, such as water, is a bi-product of the reaction.
The condensation reaction associated with the formation of the linear molecule 6-6 Nylon is illustrated opposite. The mers involved are hexa-methylene diamine and adipic acid, each of which has a six carbon atom backbone.
From: Askeland, "The Science of Engineering Materials," PWS (1994)
These mers react to create the basic building block of nylon and water is the condensation bi-product of the reaction. The nylon 'molecule' has H and OH groups at its ends and each end can continue the reaction with additional adipic acid and hexa-methylene diamine mers adding more carbon backbone and displacing water.
| Materials |
| Menu |
| Prev |
| Next |