Elastomers are amorphous polymers comprised of linear molecules that have been selectively cross linked by a 'vulcanization' reaction.
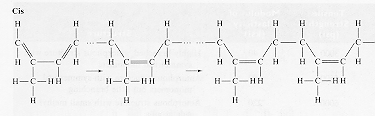
The chemistry of the isoprene molecule of natural rubber is shown opposite. Without cross linking, the condensed phase of the material behaves as a visco-elastic solid and flows under an applied stress.
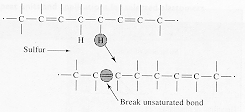
A reaction with sulphur that produces cross-linking between the isoprene chain molecules is also shown. The degree of cross linking determines the rigidity of the final material. When deforming the cross-linked material, the isoprene chains can uncoil under the applied stress and a large elastic deformation can occur. The cross-linking prevents the chains from sliding past each other and when the tensile force is removed the material returns to its original dimension.
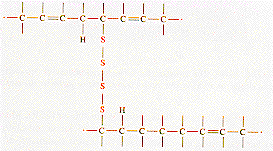
From: Askeland, "The Science of Engineering Materials," PWS (1994)
| Materials |
| Menu |
| Prev |
| Next |