Ultimate Tensile Strength
(UTS)
When
a material is deformed at constant
strain-rate, the Nominal stress/strain
curve
shows a maximum stress point in the plastic
deformation region.
Past this point the stress
required to cause an additional strain
decreases
as the strain increases.
This point, M on the diagram, is the
UTS.
In a constant load measurement of the
mechanical response
of the material, it becomes unstable at loads greater than the UTS.
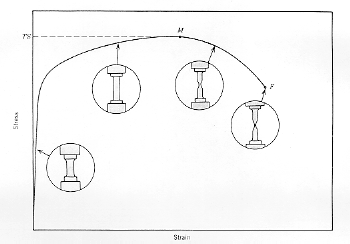
Examination of the deforming sample shows that at the UTS a "neck" forms in the material and the deformation is not uniform past this point, being concentrated in the high stress (smaller area) neck region. Ductile fracture occurs in this neck region, terminating the life of the sample. This is point F on the diagram.