| |
Motion
in a Straight Line
Abstract
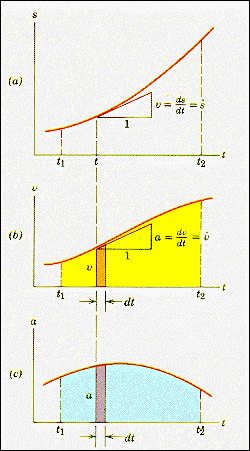
Motion in a straight line can be characterized
by parameters such as position, velocity, acceleration and their time dependence.
A bicycle will be used for these measurements and together with the rider
the system will be treated as a point mass obeying Newton's laws of motion.
The primary data collected will be the time that it takes a rider to reach
a measured distance. This data will be used to provide information about the
velocity and acceleration of the system as a function of time. From a knowledge
of the acceleration at any given time and the mass of the bike-rider system,
the net force acting on the system can be determined. After changing
the air-resistance of the bike by adding a flat plate to the handlebars, the
above quantities can be redetermined. Conclusions about the effect of air resistance
on bicycle performance can be drawn. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|