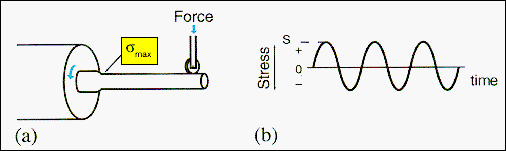| |
Spoke
material may be tested for its fatigue life properties using an apparatus of
the type shown. The spoke material is held in a colet and rotated about its
long axis. A force is applied to the free end of the spoke, causing it to bend
by a controlled amount. The stress in any small element of the spoke is
then periodic about zero as shown in (b), with the maximum amplitude, smax,
being furthest from the point of force application. One revolution
of the spoke takes the stress amplitude through one cycle.
This
test is destructive, with the spoke being rotated under constant load conditions
until it fails. The test is repeated for other "identical" samples
under the same or different load conditions, and the number of cycles
to fatigue fracture, N,
is recorded as a function of the applied stress, S. The data is then plotted on a semi-logarithmic
plot of S
v. Ln(N),
a so called S-N plot.
An important design issue is
that there is a wide spread in N for a given S, the failure being statistical
in nature and dependent upon the surface condition of the sample. |
|