|
The
work done by the force as the particle moves between points 1 and 2 on
the path is the sum of all such small elements of work: U
= S dU
= S12(Ftds).
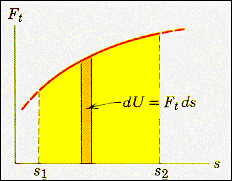
This is just the area under the plot of the tangential force as a function
of position along the path between these points as indicated in the diagram.
The SI unit of work is the Newton.meter (N.m) which is given the special
name Joule (J).
The
work done on the particle in moving between 1 and 2 increases its kinetic
energy, Ttrans = (mv2/2),
such that U = m(v22
-v12)/2 = DTtrans
. The kinetic energy depends upon the square of the velocity and, therefore,
is always a positive quantity. Its value does not depend upon the direction
of the velocity making it a scalar. In SI units it is measured in (N.m)
or Joules (J)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|