| |
The
Epicyclic gearbox
The Epicyclic
gearbox was devised in 1781 (as a sun and planet gear) by James Watt for
use in conjunction with his steam engines. The concept was adopted in 1902
by Sturmey and Archer for a multi-speed rear bicycle hub. The initial design
was for two speeds, but was rapidly developed to give a three speed gearbox.
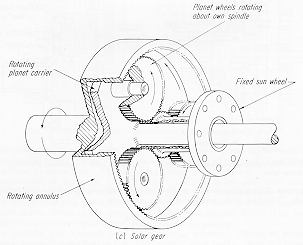
The
diagram shows the essential features of an epicyclic gearbox.
At the center is a 'Sun' gear which meshes with the three 'Planet' gears that
run on spindles on the planet carrier. These gears in turn mesh with teeth
of the outer 'Ring.' If all of the gear carriers are locked together, the input
and output shafts of the box rotate at the same rate. The overall gear
ratio would then be expressed as 1:1. Fixing the planet gear carrier and allowing
independent rotation of the sun and ring gears gives them a relative rotation
rate determined by their tooth counts, NS and NR.
This overall gear ratio is:
Gear
Ratio1 = (NR / NS). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|