|
|
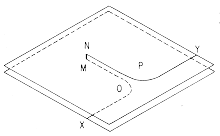
A
dislocation dipole has two dislocations of opposite sign that are on different
slip planes separated by an atomic scale distance. The diagram shows a
dipole (MO and NP) generated when the jog MN is unable to follow the moving
dislocation XY as it glides on the two slip planes. If MN one atomic spacing
high, the dislocation dipole is a row of interstitial atoms if OM and MP
are edge dislocation sections of opposite sign with their extra half planes
"inside" the dipole, or a row of
vacancies if the extra half planes lie
outside the dipole. If OM and MP are mixed dislocations, the interstitials
or vacancies will not occur at every lattice site along the dipole but
at intervals that depend on the angle between the Burgers vector and the
line vector of the mixed dislocations.
The
transmission electron microscope photograph shows a dislocation dipole
in a cadmium crystal for which the (0001) plane is the slip plane. The
length of the dipole shown is about 2 microns. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|