|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| When
a material is mechanically excited, compression/tension waves or shear
waves can be propagated from the point of excitation. These elastic waves
move through the material with a velocity determined by its elastic modulus
and its density, r.
For
longitudinal waves this velocity is the sound velocity, c, and CL
= (E / r)0.5,
where E is Young's modulus. For shear waves the controlling elastic modulus
is the shear modulus, G. For shear waves: CS
= (G / r)0.5.
|
|||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| From: Kittel, "Introduction to Solid State Physics," Wiley (1971) | |||||||||
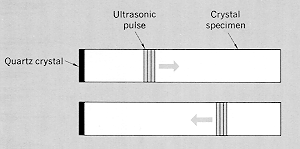
| The diagram illustrates a method for launching elastic waves using piezoelectric quartz transducers to produce the excitation, and then as detectors for the reflected elastic wave. The density discontinuity at the end of the sample is responsible for the reflection. The transit time for the elastic wave may be measured with high precision and the wave velocity can be accurately determined. The illustrated system is a good method for measuring the elastic constants of materials. | |||||||||