|
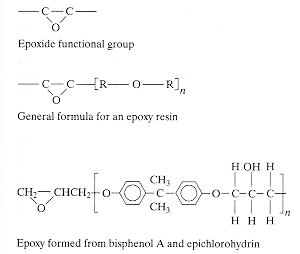
Epoxies
are thermosetting polymers, named for the epoxide functional group that
is present in the polymers. Curing is initiated by a catalyst which becomes
part of the final material with no condensation products being released.
The final material has a three- dimensional network structure that makes
it rigid. The degree of shrinkage upon cure is small (0.01%) and these
materials can be moulded to near net shape. Low shrinkage also makes them
good adhesives. They are stable against decomposition to about 175 C.
Epoxies are used as matrix materials for many composite materials. Their
initial low viscosity liquid state makes it easy to impregnate a fiber
matrix, the good adhesive properties after cure provide strong coupling
between the fibers and the matrix, and the low shrinking during cure does
not put the fibers into compression. Epoxies have a density of circa
1.3 Mg/m3, Young's
modulus of 4 GPa, UTS of 60 MPa, elongation to fracture of 3%, and thermal
expansion coefficient of 60 x 10-6/C. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|