|
A
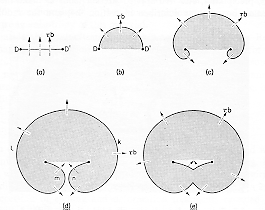
Frank-Reed source permits the dislocation multiplication required for slip
in crystalline solids. The sequence of source operation is shown and results
in the shedding of a dislocation loop and regeneration of a dislocation
that can repeat the sequence. In the absence of a stress field a
dislocation will straight (a). A segment is shown between two pinning
points, D and D'. In a stress, t,
the dislocation experiences a force per unit length
tb and the balance between
this force and the line tension of the dislocation causes curvature.
In (b), the minimum radius, R = L/2, where L is the distance D-D'.
The stress, tcr,
required to establish this radius is the critical shear stress of the sample.
When the applied resolved shear stress is larger than tcr
the dislocation loop expands and its radius again increases (c).
The stress force is always normal to the dislocation line, and the loop
closes on itself (d). The two segmentsof opposite sign, m and n,
collide and annihilate generating a free loop (e) and a new dislocation
segment to repeat the sequence. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|