|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| When
heat treating a ferrous alloy it is necessary to start from a known thermodynamic
condition of the alloy. This condition is established by heating the alloy
above the eutectoid temperature and converting it to a homogeneous austenite
phase. This material is then air cooled to room temperature to produce
a two phase mixture of a-Fe
(ferrite) and Fe3C (cementite). After this treatment the alloy
is said to be normalized.
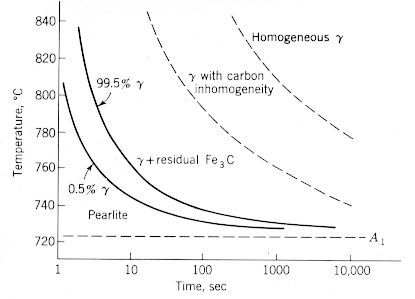
The diagram shows the T-T-T diagram for the formation of austenite. If 800 C is used as the austenizing temperature, the material should be held at this temperature for about 10,000 sec (3 hours) to reach a homogeneous state. |
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
| From:
Brick, Pense and Gordon,
" Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys" McGraw Hill (1997) |
||||||||||