|
Rubber
is the general term for an elastomer, a polymeric material that may be
deformed elastically by several hundred percent. Elastomers are based on
macromolecules with either carbon or silicon backbones that have been crosslinked
with sulphur atoms. The crosslinking prevents relative sliding of the macromolecules
and helps the structure return to its initial dimensions after elastic
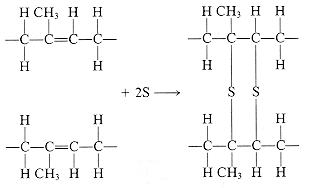
deformation. The diagram shows the vulcanization reaction for the polyisoprene
elastomer. The double bonds in the backbone of two adjacent molecules are
opened up and sulphur crosslinks are established between the molecules.
Typically 1wt % to 5wt % sulphur is used in the vulcanization process.
The
degree of crosslinking determines the rigidity of the elastomer, the elastic
modulus being directly dependent on the crosslink density. At very high
cross link densities the material becomes rigid. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|