|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
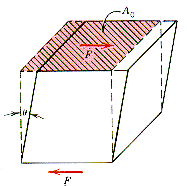
| The
diagram shows a force, F, applied tangientially to a surface of area, A0.
The shear stress, t,
produced by this configuration is given by: t
= (F/A0).
If the material is linear elastic, the effect of this applied shear stress
in the elastic range will produce a shear strain, g
= tan q.
The stress and strain are coupled through the Hookian elastic relationship,
t
= Gg,
where G is the shear modulus of the material.
For an isotropic elastic continuum, the shear modulus, G, is related to Young's modulus, E, and Poisson's ratio, n: G = E/2(1 + n) |
||||||||||
 |
||||||||||
| From:
Callister,
"Materials Science and Engineering," Wiley (1994) |
||||||||||