|
Silicon
dioxide can exist in both crystalline (quartz) and amorphous (fused silica)
forms. The crystalline has three polymorphic forms: crystobalite, tridymite,
and quartz. Crystobalite is the high temperature polymorph with a cubic
zinc-blend structure, monoclinic tridymite is stable at intermediate temperatures,
and quartz, the low temperature polymorph, is hexagonal. The structural
transformations between these crystal forms are slow and they may all exist
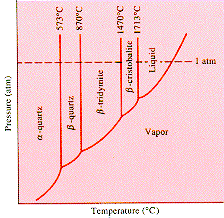
at room temperature. The diagram is a pressure-temperature phase diagram
for SiO2. The transition
between a-quartz
and b-quartz
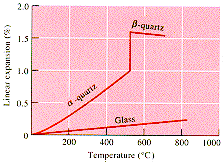
is accompanied by a large volume change. This is shown in the lower diagram
which also indicates that b-quartz
has a negative thermal expansion coefficient. In contrast to this behavior
the amorphous (glass) form of silica shows a continuous positive thermal
expansion coefficient.
Quartz
is an important optical material with a refractive index of 1.55 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|