|
|
The
surface energy of a material is a measure of the increase in Gibbs function
of the material per unit area of surface created: g
= (dG/dA)T,p,n
,
it
being assumed that the ambient is a vacuum . In a crystalline material,
the free energy change is associated with the change in lattice spacing
in the surface region.
If
the surface created is in contact with a gas, liquid or solid, the interfacial
surface energy will be different from the vacuum value. The interfacial
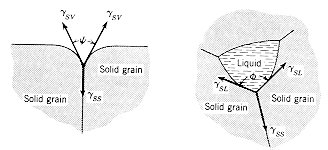
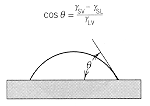
energy balance at the contact region will determine the allowed angle of
wetting for a liquid on a solid surface, and the angle between grain boundaries
in a polycrystalline material. These effects are illustrated below. |
|