|
|
|
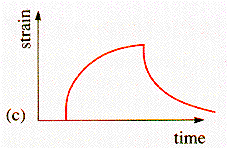
A
viscoelastic material is one that shows a time dependent strain response
to a step change in applied stress. Diagram (c) shows strain v. time and
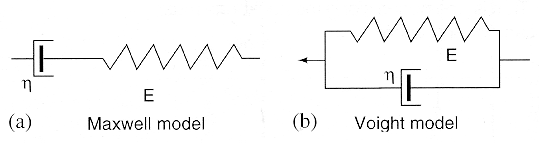
is the response of the material to a Heaviside function stress. Two models,
(a) the Maxwell model, and (b) the Voight model provide a mechanical interpretation
of this behavior.
The
Voight model is best model for the response shown in (c). The step increase
in stress is applied to a spring constrained by the viscous damper. The
spring only reaches its equilibrium length under the applied stress after
some time. Upon removal of the stress, the spring is prevented from immediately
returning to its original length by the damper and reaches zero extension
with the same relaxation time as that shown during loading.
The
Maxwell model is a better description of creep behavior in a viscoelastic
material. If a step strain is applied to the system a stress condition
is established in the spring. If the strain is kept constant, the series
damper moves and relaxes the stress in the spring. Removal of the external
interaction leaves the system in a strained condition. |
|
|