In tension a stay is stable except for plastic deformation when the yield stress is passed. In compression another event, buckling, may determine the design limit for load.
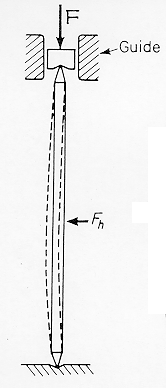
The diagram shows a strut
of length, L, being loaded in compression by a force, F. The system is
stable against small sideways displacements until the force F reaches some critical
value:
FC = {n2
p2 E A2 / 4 L2
}
where the rod is assumed to be circular in cross section
with an area A. Once FC is passed, the rod buckles and the section
is considered to have failed. The lowest value of FC is for
n = 1.
If the strut is slender enough (i.e. {A/L} is small enough),
the buckling force will correspond to a stress, (FC / A), that is
less than the yield stress of the material. For this case, buckling occurs
before the elastic limit of the material is reached.
From: Polakowski and Ripling, "Strength and Structure of Engineering Materials," Prentice Hall (1966)
| Materials |
| Menu |
| Prev |
| Next |