The material selection for such a strut is based on the lightest structure of a given length. The mass, M = rAL, and substituting this in the expression for the buckling force gives: (FC / M2 ) = (E / r2 ){p / 4L2 }. Selection is then based on maximizing the value of (E / r2 ).
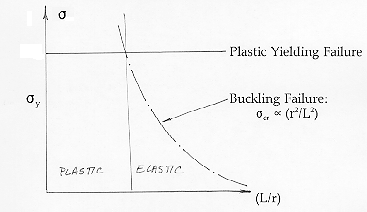
The diagram illustrates
how the two failure modes, buckling and plastic deformation, depend upon the
length to radius ratio of the strut. For a short strut, for which (L / r)
is small, the failure is by plastic deformation in compression. For a long
strut the failure mode is by Euler buckling.
For the same mass of material,
the buckling stability range can be changed by altering the shape of
the strut. A hollow tube of larger radius will be more stable than a solid
rod of smaller diameter.
| Materials |
| Menu |
| Prev |
| Next |