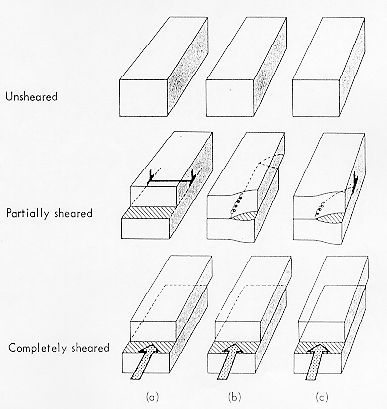
The diagram shows the effect of 'sliding' an Edge (a), Screw (b), or Mixed (c) dislocation completely across a slip plane in the crystal. Each dislocation has the same effect; it displaces the top of the crystal with respect to the part below the slip plane by a 'ruck size' characteristic of the dislocation. This size is known as the Burgers vector of the dislocation. The Line direction of each dislocation is shown. For an Edge, the Burgers vector and the line are perpendicular and in the slip plane. For the Screw they are parallel, and for the Mixed dislocation each section of the line makes a different angle with the Burgers vector.
From: Barrett, Nix,
and Tetelman, "The Principles of Engineering Materials,"
Prentice Hall (1973)
| Materials |
| Menu |
| Prev |
| Next |