| |
|
Brakes
Brakes are designed
to dissipate the kinetic energy of a moving bicycle so that its speed
can be controlled. Most common brakes use the wheel rim as one of their elements.
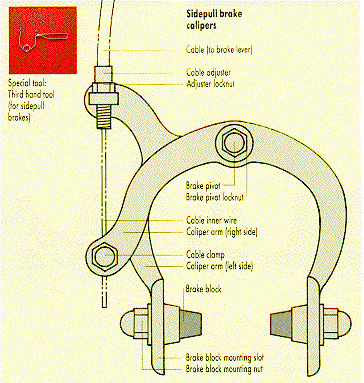
The
caliper design of side-pull brakes is illustrated. The brake
pivot attaches the calipers to the frame and each arm can move independently.
The cable transmits force from the handlebar mounted brake lever, and the
caliper design splits this force equally between the two arms. The two brake
blocks are of friction material and these make contact with the wheel rim.
The block surface may have drainage grooves to remove water from a wet rim. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|