| Corrosion & Environmental Degradation |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
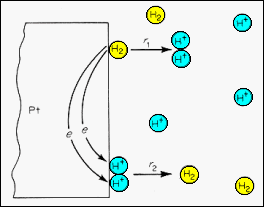
| ·The
hydrogen reference electrode uses platinum metal as a solid surface upon
which the electron exchange interactions can take place between hydrogen
atoms and hydrogen ions.
H2 <-> 2H+ + 2e · This is a "reversible electrode." The metal is inert in this electrolytic ambient and only serves to facilitate the required electron exchange reactions. ·The electrode potential associated with the reaction is set as Zero at STP and a molar concentration of H+ ions in the electrolyte. This condition provides a defined zero point against which other potentials can be measured. ·In the steady state, the rates of the two directions of the reaction, r1 and r2 , are equal. |
|||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||
| From:
M.G. Fontana,
"Corrosion Engineering," Wiley (1986) |
|||||||||||||||